Uveitis
Navigating Uveitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Medications and Vision Preservation
Uveitis, an inflammation of the uvea—the middle layer of the eye—presents unique challenges to ocular health. This condition demands a nuanced approach, and medications tailored for Uveitis play a pivotal role in alleviating symptoms, managing inflammation, and safeguarding the delicate structures of the eye. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the importance of Uveitis medicine, shedding light on the intricacies of treatment and the impact on vision preservation.
Understanding Uveitis:
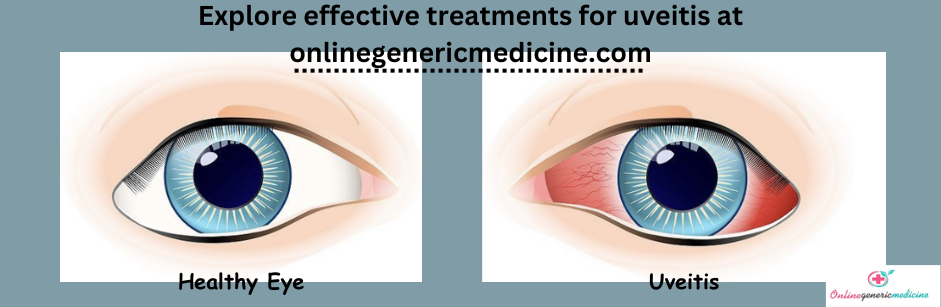
Uveitis is characterized by inflammation of the uvea, which comprises the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. This inflammation can affect the eye's structures, leading to pain, redness, light sensitivity, and potential vision loss. Uveitis is a broad term that encompasses various subtypes, each with its own characteristics and potential causes.
The Importance of Uveitis Medications:
- Controlling Inflammation: Uveitis medications are designed to control and reduce inflammation within the eye. Inflammation is a hallmark of Uveitis and can cause damage to ocular tissues if not addressed promptly. Medications play a crucial role in modulating the immune response to manage inflammation effectively.
- Alleviating Symptoms: Pain, redness, and light sensitivity are common symptoms of Uveitis that can significantly impact daily life. Medications help alleviate these symptoms, improving the overall comfort and well-being of individuals affected by Uveitis.
- Preserving Vision: Vision preservation is a primary goal in Uveitis management. By addressing inflammation and preventing complications, medications contribute to maintaining visual acuity and preventing long-term vision impairment.
Types of Uveitis Medications:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications are often prescribed in the form of eye drops, injections, or oral tablets. Corticosteroids help suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation within the eye.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: In cases of severe or chronic Uveitis, immunosuppressive drugs such as methotrexate, azathioprine, or cyclosporine may be prescribed to modulate the immune system and control inflammation.
- Biologics: Biologic medications, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, are used in some cases to target specific inflammatory pathways involved in Uveitis.
Antiviral or Antibacterial Medications: If Uveitis is caused by an infection, antiviral or antibacterial medications may be prescribed to treat the underlying microbial cause.
Treatment Approaches and Combination Therapies:
The choice of Uveitis medication depends on the type, severity, and underlying cause of the inflammation. In some cases, a combination of medications may be used to achieve optimal control of inflammation. The treatment plan is often tailored to the individual needs of the patient.
Routine Monitoring and Adjustments:
Managing Uveitis is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring. Eye care professionals assess the response to medications, monitor intraocular pressure, and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. Routine follow-up appointments are crucial for long-term success in Uveitis management.
Patient Education and Adherence:
Educating individuals about the importance of adherence to prescribed medications is key to successful Uveitis management. Patients need to understand the potential risks of untreated inflammation and the role medications play in preserving their vision.
Addressing Underlying Causes:
In some cases, Uveitis may be associated with underlying systemic conditions, such as autoimmune diseases or infections. Addressing these underlying causes, when present, is essential for comprehensive Uveitis management.
Coping Strategies and Support:
Living with Uveitis can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Support groups, counseling, and coping strategies contribute to a holistic approach to Uveitis care, helping individuals navigate the complexities of their condition.
Conclusion:
In the intricate tapestry of ocular health, Uveitis medications emerge as guardians, standing against the tide of inflammation to preserve vision and enhance the quality of life for those affected. By understanding the importance of these medications and embracing a collaborative approach with healthcare professionals, individuals with Uveitis embark on a journey towards vision preservation, resilience, and a future filled with clarity and sight.



