Meniere's Disease
-
Generic: CinnarizineEquivalent Brand: Avidazine50 Tablet/s$17.00
Navigating the Waves of Meniere's Disease: The Crucial Role of Medications in Symptom Management
Meniere's Disease, a chronic condition affecting the inner ear, brings with it a symphony of symptoms that can disrupt one's equilibrium and quality of life. Understanding the importance of medications tailored for Meniere's Disease is fundamental in mitigating symptoms, enhancing daily functioning, and providing individuals with the tools to regain control over their well-being.
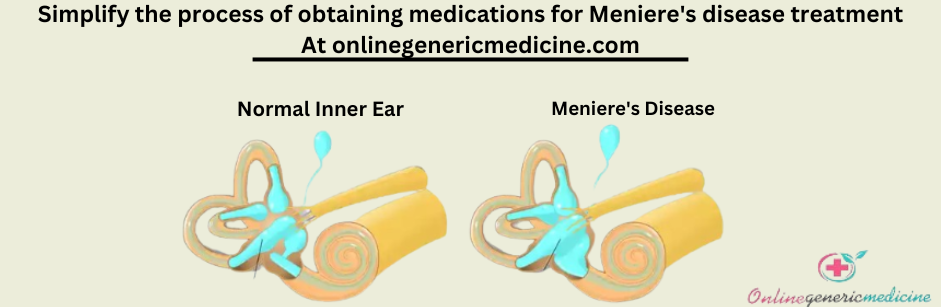
Understanding Meniere's Disease:
Meniere's Disease is characterized by a combination of symptoms, including vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the affected ear. The exact cause of Meniere's Disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve fluid buildup in the inner ear, leading to disturbances in balance and hearing.
The Role of Medications in Meniere's Disease:
- Managing Vertigo: Vertigo, the hallmark symptom of Meniere's Disease, can be debilitating and impact daily activities. Medications, such as vestibular suppressants and antiemetics, are often prescribed to manage vertigo episodes and alleviate associated nausea.
- Controlling Fluid Buildup: Diuretics, a class of medications that increase urine production, are commonly used to control fluid retention in the inner ear. By reducing fluid buildup, diuretics help alleviate symptoms such as vertigo and pressure in the ear.
- Addressing Tinnitus: Tinnitus, the perception of ringing or buzzing in the ears, is a common and distressing symptom in Meniere's Disease. Medications, along with other management strategies, can help address and alleviate the impact of tinnitus on a person's daily life.
Types of Medications for Meniere's Disease:
- Diuretics (Water Pills): Diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide or acetazolamide, are often prescribed to reduce fluid retention in the inner ear, helping to control symptoms.
- Vestibular Suppressants: Medications like meclizine or diazepam may be prescribed to suppress the vestibular system, reducing dizziness and vertigo.
- Antiemetics: Antiemetic medications, such as ondansetron or promethazine, help control nausea and vomiting associated with vertigo episodes.
- Corticosteroids: In some cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications and Medication Adherence:
In addition to medications, individuals with Meniere's Disease often benefit from lifestyle modifications. These may include dietary changes, stress management, and physical therapy. Adherence to prescribed medications and lifestyle recommendations is essential for long-term symptom management.
Hearing Preservation and Rehabilitation:
Given that hearing loss is a common component of Meniere's Disease, hearing preservation and rehabilitation strategies are integral. Hearing aids and assistive listening devices may be recommended to improve communication and quality of life.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals:
The management of Meniere's Disease is highly individualized, and healthcare professionals play a crucial role in tailoring treatment plans to the specific needs of each patient. Regular follow-up appointments allow for adjustments to medications and interventions based on the progression of the condition.
Support and Coping Strategies:
Living with Meniere's Disease can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Support groups, counseling, and coping strategies are valuable components of a holistic approach to managing the impact of the condition on one's overall well-being.
Conclusion:
In the journey of navigating the unpredictable waves of Meniere's Disease, medications emerge as essential allies in symptom management. By understanding the importance of these medications, individuals can take proactive steps towards regaining control over their lives, minimizing the impact of symptoms, and embracing a future where the challenges of Meniere's Disease are met with resilience and empowerment.



